WEALTHFOUNDATION
What Is Estate Planning?
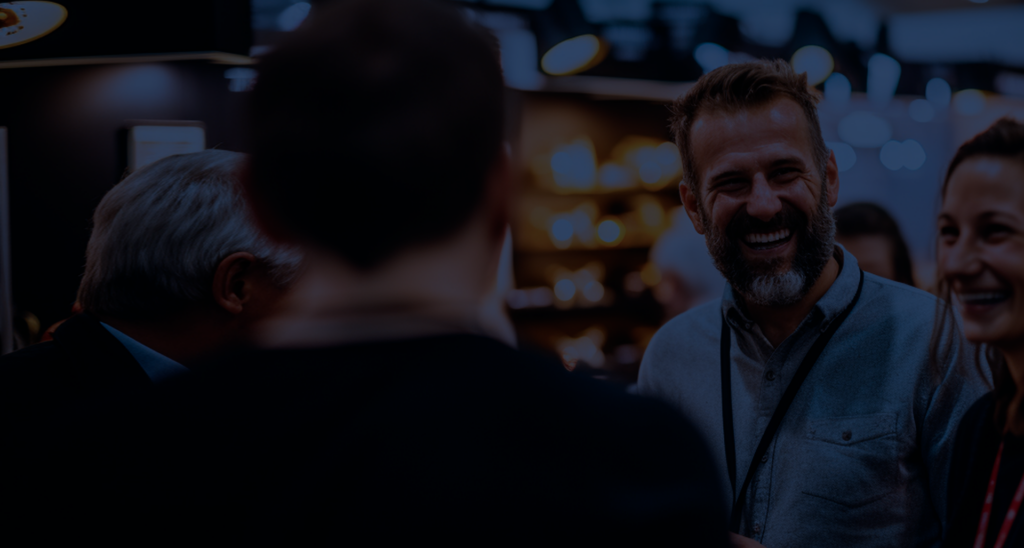
Estate planning is the process of preparing your estate and designating who is entitled to your assets following your death or incapacitation. The estate planning process is usually done in coordination with an estate planning attorney to ensure your plan is legal while protecting both your assets and the beneficiary’s best interests.
Working with an adviser who understands your assets and financial goals can make estate planning easier. How you structure your estate can affect the probate and fees associated with transferring your assets.
Many of the estate planning steps will depend on your assets. However, key things to cover when estate planning include:
Instructions for your care in the event you become ill or incapacitated
Directions for transferring any businesses you own
Who will care for your children upon your death
Directions for disability income insurance if you’re unable to work
Guardianship for minor children until they reach legal age
Information on where beneficiaries can find important asset information
Qualify to receive a complimentary estate planning consultation
FEATURED IN
Important Things to Consider When Estate Planning
Also, consider the tax implications of your assets. Beneficiaries might face expensive taxes, court fees, or legal costs following your death. Reviewing this ahead of time with an estate planner can help minimize these costs.
Depending on your assets, the associated fees can be high. A goods and services tax, for example, which often skips generations, can be as high as 40%. Considering tax and legal implications ahead of time allows you to maximize the assets you leave behind.


Who Needs Estate Planning?
Everyone needs estate planning. While older individuals or those close to retirement might want to think about estate planning sooner, it’s never too early to plan and protect your loved ones.
A common misconception is people with limited income don’t need estate planning. These families, however, stand to benefit most from a lost loved one’s assets. If you don’t create a living will or a living trust and you become incapable of managing your own assets, the state might assign a conservatorship or guardianship on your behalf. Upon your death, the state will disperse your assets based on its intestacy laws.
Estate planning is a necessary part of life, regardless of your age or wealth. Are you ready to protect your assets and loved ones?
Assigning a Directive During Estate Planning
Assigning directives or roles is important when estate planning. Directives to consider include:
Power of Attorney
A power of attorney lets someone manage your assets if you can’t. It authorizes them to act on your behalf in legal or financial matters. A limited power of attorney is temporary and clearly defines what the person can and cannot do.
Health Care Proxy
A health care proxy designates someone to make medical decisions for you if you cannot. Often part of an advance directive, it’s sometimes called a durable power of attorney. The proxy may also handle personal items left at the hospital and authorize medical procedures.
Living Wills and Probate
Unless you create a living trust, your assets might go through probate. It’s important to consider what probate means and how it might affect the distribution of your assets.
What Is Probate?
Probate is a process in which an executor oversees the distribution of a person’s will and assets upon their death. This legal process involves reviewing assets and estate information. In most cases, a probate court also reviews the transfer of assets.
Creating a will allows you to manage your assets and distribute them as you see fair. Without a revocable trust, however, probate law means the court also gets to rule. Many people prefer to create a revocable living trust, as it allows beneficiaries to avoid probate.
What Does it Mean When a Will Is in Probate?
To probate a will means it must go through a court-supervised legal proceeding. During probate, the court will review the authenticity and validity of the will. The court will distribute assets to each beneficiary and make rulings about disagreements. A will might stay in probate for a couple of months to a few years, depending on the number and value of assets.
What Is Probate in Real Estate?
The probate definition when it comes to real estate is a legal process that allows a living will to transfer ownership of property to another person. Probate essentially means to prove. Real estate is one of the most common assets included when estate planning. A living will lists who receives your real estate assets. However, your real estate assets must still go through probate. Some states require multiple probate sessions for the transfer of real estate.

What Is a Living Trust?
A living trust is a fiduciary agreement that allows you to give instructions on how to disperse your assets upon death. Living trusts are most commonly used in the form of a revocable agreement that allows the family to skip probate.
What Is a Living Revocable Trust?
A trust is a legal directive that assigns your assets to a loved one while you’re still alive. This might be necessary when you’re incapacitated or unable to make decisions, which then allows your designated person to take over without having to go through the probate process. An irrevocable trust is similar to a revocable living trust, except it can’t be changed.

Difference Between Living Trust vs. Will
A living trust, once signed, notarized, and funded, is a legally binding document that guarantees your plan for your estate will be executed as you wish. This is the confidence that a will cannot provide because, even though it is a legal document, it is subject to probate, where it is scrutinized and can be threatened.
Living Trust
Will
Prepared by a lawyer
Distributes your assets to family and loved ones
Titles assets directly into it for ease of distribution
Appoints a guardian for your minor children
*
Deal with all of your property under the laws of the state you choose, rather than under separate probates in each state where the property exists
Maintains privacy and confidentiality; not a matter of public record
Trustee retains control of the distribution of property, rather than a judge
Assets can be distributed without the cost of hiring a lawyer for lengthy and costly probate proceedings
*When a pour-over will is included. Anderson includes a pour-over will with all of their living trusts.
Difference Between Living Trust vs. Will
A living trust, once signed, notarized, and funded, is a legally binding document that guarantees your plan for your estate will be executed as you wish. This is the confidence that a will cannot provide because, even though it is a legal document, it is subject to probate, where it is scrutinized and can be threatened.
|
Features
|
Living Trust
|
Will
|
|---|---|---|
| Prepared by a lawyer | ||
| Distributes your assets to family and loved ones | ||
| Titles assets directly into it for ease of distribution | ||
| Appoints a guardian for your minor children | ||
| Deal with all of your property under the laws of the state you choose, rather than under separate probates in each state where the property exists | ||
| Maintains privacy and confidentiality; not a matter of public record | ||
| Trustee retains control of the distribution of property, rather than a judge | ||
| Assets can be distributed without the cost of hiring a lawyer for lengthy and costly probate proceedings |
ANDERSONADVISORS
Trusted Advisors. Proven Results. Real Protection.
Anderson Business Advisors services provide the pathway to prosperity with unmatched precision and tailored solutions to meet your unique investment journey.
157K
SATISFIED CLIENTS SERVED
277K
BUSINESS CREATED
$150M
IN CLIENT TAX SAVINGS
$1B
IN ASSETS PROTECTED